Blockchain technology has ushered in a new era of trust and transparency, and Ethereum stands at the forefront of this revolution. One of the key developments within the Ethereum ecosystem is the Ethereum Attestation Service (EAS). In this comprehensive blog, we will delve deeper into the Ethereum Attestation Service, explore its significance in enhancing trust, and uncover a wide array of compelling use cases that demonstrate the versatility and potential of this groundbreaking service.
What are Attestations and their Role in Ethereum
Attestations (digital records or evidence of information made by anyone about anything) play a crucial role in Ethereum’s consensus mechanism, specifically in the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) protocol. Validators, who participate in securing the network, are responsible for creating, signing, and broadcasting attestations during each epoch, which lasts approximately 6.4 minutes.
These attestations serve as votes that reflect a validator’s view of the Ethereum blockchain, including the most recent justified block and the first block in the current epoch. By collectively attesting to the validity of blocks, validators contribute to the consensus process, bolstering the overall security and integrity of the network.
The service was announced to go live on the mainnet by a tweet thread, which explained the vision behind the service. “The concept of identity is abstract, and existing solutions have attempted to define and demonstrate it, yet fell short.” Hence, the journey with EAS began with the goal of solving the on-chain identity problem, which has prevailed since the inception of Ethereum.
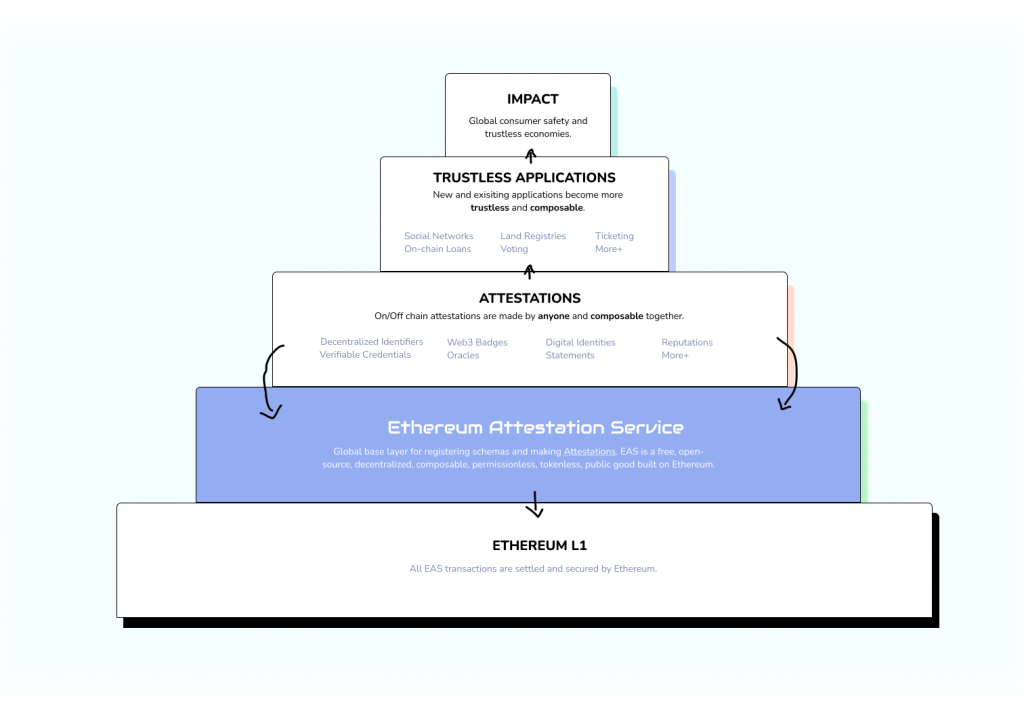
Being an open-sourced and decentralized service, EAS does not presuppose anything or make assumptions of it being used for the appropriate schema structure for a particular use case. The primary objective of EAS is to build more trust, and it aims to be the Global base layer where anything can be attested. The creators behind EAS envision empowering the world by delivering a global, open, and interoperable attestation layer.
Use Cases of Ethereum Attestation Service:
Identity Verification and Decentralized Identity (DID)
The Ethereum Attestation Service can play a vital role in identity verification and establishing decentralized identity systems. Individuals can securely prove their identity without relying on centralized authorities by creating on-chain attestations linked to specific identity attributes. This has immense potential in various sectors, such as decentralized finance (DeFi), healthcare, and digital identity platforms.
EAS plays a vital role in Optimism ~ a layer two solution on Ethereum by providing a mechanism for creating, verifying, and revoking on and off-chain attestations. These attestations serve as cryptographic proofs of the validity of transactions and computations on the Optimism network.
Validators within Optimism are responsible for creating, signing, and broadcasting these attestations during each epoch. Through EAS, validators can securely attest to the correctness of the Optimism blockchain and contribute to the consensus process. Find more about Optimisim’s integration with EAS to promote users’ trust here.
Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Attestations can be used to verify and validate information related to supply chains, ensuring transparency and traceability. By creating attestations regarding product origin, quality, and authenticity, stakeholders can establish trust among participants and consumers. This has significant implications for the food, pharmaceuticals, and luxury goods industries.
Intellectual Property Protection
With the Ethereum Attestation Service, creators and innovators can attest to the ownership and authenticity of their intellectual property, including digital assets such as Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). These attestations serve as tamper-proof evidence of ownership, enabling artists, musicians, and content creators to protect their creations and establish provenance.
Data Integrity and Auditing
Attestations can be utilized to verify the integrity and accuracy of data, making it suitable for auditing purposes across various industries. Financial records, medical data, and legal documents can be attested on-chain, providing an immutable and transparent record that enhances trust and accountability.
Governance and Voting Systems
The Ethereum Attestation Service can be leveraged to enable secure and transparent governance and voting systems. Organizations and communities can ensure fair and auditable decision-making processes by creating on-chain attestations linked to voting decisions or proposals.
Insurance and Claims Processing
Insurance companies can utilize attestations to verify claims and streamline the claims processing workflow. By creating on-chain attestations related to events or conditions covered by insurance policies, the verification process can be expedited, reducing administrative costs and enhancing trust.
Real Estate Transactions and Title Verification
The Ethereum Attestation Service can revolutionize the real estate industry by providing secure and transparent title verification. Attestations can be used to prove ownership, transfer property rights, and validate the authenticity of property-related documents, streamlining the transaction process and reducing the risk of fraud.
On-Chain vs Off-Chain Attestations
Just like transactions, attestations can be done on-chain, where the data is stored directly on Ethereum, and off-chain, where the data is stored off-chain or outside the blockchain network on a decentralized storage system, like IPFS or in a browser as a URL hash. Let’s understand the key differences between the two:
| Basis | On-chain Attestations | Off-chain Attestations |
| Timestamp | Published on Blockchain with a guaranteed timestamp | Stored on decentralized off-chain storage solutions like IPFS, do not have a guaranteed timestamp. |
| Verification | Verifiable by Smart Contracts | Verification of the attestations is done via digital signatures represented on-chain |
| Fees | Require a gas fee for storing data on-chain, making it an expensive affair to store heavy data. | No gas fee for storing the data off-chain, hence more affordable and scalable when dealing with big data chunks. |
| Use-cases | Use cases include oracles, on-chain identity verification, KYC validation for exchanges, enhancements to SBTs, reputation systems, credential verification, and 2-factor authentication for Dapps. | Use cases include ticketing, licenses, passports, document verification, voting, healthcare records, and social media messages. |
| Security | Require consensus on the Ethereum network, making it highly secure. | Do not require consensus resulting in a lower level of security. |
| Accessibility | Publicly accessible, hence not suitable for storing sensitive information. | Can be public or private, offer more control over the visibility & privacy to the attestation. |
Conclusion
The Ethereum Attestation Service represents a significant milestone in the Ethereum ecosystem, enabling trust, transparency, and decentralization. With its ability to create, verify, and revoke on and off-chain attestations, EAS is set to unlock many use cases across various blockchains and Dapps.
EAS being available as a public good directly contributes to bolstering the fundamentals of blockchain in terms of decentralization, and aims to promote significant incentives for value creation and extraction to be built.













