Quick Links
In very simple terms, Insurance is a type of risk management tool that provides financial protection against unforeseeable events such as accidents, illnesses, and natural disasters. It works by transferring the risk of loss from an individual or organization to an insurance company in exchange for a premium. Insurance is essential because it helps protect people from the financial consequences of unexpected events. In this blog, we will cover three generations of insurance starting from mutual aid insurance to the usage of blockchain in insurance. We will understand how insurance methods started with a decentralized structure, to a centralized one, and again to a decentralized structure.
The History of Insurance
Insurance has a long and rich history that can be traced back to ancient civilizations. In the medieval period, insurance was used to cover losses from the voyages of ships and their cargo. This was the first generation of insurance, which relied on a system of mutual aid, where members of a group would pool their resources to provide insurance coverage for each other.
Following this, insurance was introduced in many states and regions where people used to pool their money in case a person from the community died to give him/her a proper burial ceremony or pay for any losses in case of robbery or theft. In this, insurance claims were in hands of the people and not a central authority
Before moving ahead with the second generation or the generation of insurance provider entities, lets us understand how insurance companies work and how they make money.
Insurance companies assess the risks of various events happening and calculate the likelihood of a loss occurring. Based on this risk analysis, they set premiums for their policies, which represent the amount of money policyholders pay to maintain their insurance coverage.
- Insurance companies make money by collecting more in premiums than they pay out in claims and expenses. The difference between the premiums collected and the claims paid out is called the underwriting profit or loss. To make a profit, insurance companies aim to accurately assess the risks and set premiums that will cover the potential losses while still being affordable for policyholders.
- Insurance companies also invest the premiums collected to generate additional income. The investments are typically made in a variety of financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. The profits from these investments are called investment income.
- Finally, insurance companies also charge fees for their services, such as administrative fees, policy fees, and late payment fees. These fees contribute to the overall revenue of the company.
The second generation of insurance began with the introduction of insurance provider entities and digital technology. Digital insurance, also known as Insurtech, uses technology such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of insurance products and services.
Technology has significantly impacted the insurance industry, including the emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). In my previous response, I mentioned a few ways technology has helped insurance companies, but specifically in regards to AI and ML, here are a few examples:
- Improved fraud detection: Insurance fraud is a significant problem that costs insurers billions of dollars each year. However, with AI and ML, insurers can now more effectively identify fraudulent claims. ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, flagging suspicious claims for further investigation.
- Enhanced underwriting accuracy: AI and ML algorithms can analyze customer data and risk factors to provide more accurate risk assessments, improving underwriting accuracy. Insurers can use this data to price policies more accurately and customize coverage to meet the specific needs of their customers.
- Automated claims processing: AI and ML can automate claims processing, improving efficiency and reducing costs. For example, insurers can use image recognition algorithms to process claims for car accidents or property damage more quickly and accurately.
- Personalized customer service: AI and ML can help insurers deliver personalized services to customers. Chatbots, for example, can use natural language processing to answer customer questions and provide support 24/7.
In my interview with Mr. Sanidhya Raghvanshi (Risk Analyst at Risk Management Solutions (RMS), a Moody’s Analytics company), who works in the insurance industry, he highlighted how machine learning is transforming the industry. He mentioned how ML algorithms are being used to identify new insurance products and services, improve pricing strategies, and better understand customer behaviour. He also talked about how insurers are using ML to improve risk assessment and fraud detection, helping them to minimize losses and provide better services to their customers.
The third generation of insurance is blockchain insurance. Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger that allows for secure and transparent transactions without the need for a central authority. Blockchain insurance can be divided into two categories: tracking of insurance through blockchain and DeFi insurance.
Tracking of Insurance through Blockchain
Tracking of insurance through blockchain is the use of blockchain technology to improve the transparency and security of insurance transactions. It allows for the tracking of insurance policies from creation to execution, making it easier to detect fraud and reduce administrative costs. Additionally, it allows for the sharing of data between insurance companies, which can lead to better risk assessment and more accurate pricing.
Blockchain technology also allows for the creation of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts that automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met. Smart contracts can be used to automate the claim process, reducing the time and cost associated with manual claims processing. Usually, the claims are processed through the community of the protocol also known as DAO, which takes relevant decisions when approval for the claim is needed.
Some examples include
Health insurance
With blockchain technology, medical records can be cryptographically secured and shared between health providers, increasing interoperability in the health insurance ecosystem.
Reinsurance
By securing reinsurance contracts on the blockchain through smart contracts, blockchain technology can simplify the flow of information and payments between insurers and reinsurers.
Life insurance
Blockchain technology can take the burden of filing a death claim away from family members by replacing the manual process of filing claims with an automated system built on a blockchain ledger.
Travel insurance
By automating claims processes and efficiently sharing information between stakeholders, blockchain travel insurance can save insurers time while reducing the burden on travelers.
DeFi Insurance
DeFi insurance is a type of insurance that uses decentralized finance (DeFi) technology to provide insurance coverage. DeFi is a system of financial applications that operates on a decentralized blockchain network. DeFi insurance is designed to provide coverage for DeFi platforms, which are vulnerable to hacks and security breaches.
DeFi insurance works by allowing users to pool their funds together to provide coverage for DeFi platforms. These funds are then invested in DeFi protocols, which generate returns that can be used to pay out claims. DeFi insurance platforms use algorithms to determine the risk of the platform being hacked or compromised, and adjust premiums accordingly.
Insurance in DeFi Staking Protocols
Staking is a process in which users lock their tokens in a smart contract to support the network and earn rewards. In staking, users pool their tokens to create a pool that supports the network. However, there is always a risk involved in staking, as the tokens are locked and cannot be easily withdrawn. In the event of an attack or a bug in the smart contract, the staked tokens could be lost.
To safeguard against these risks, staking protocols can use insurance to protect their pools. The insurance would cover any losses incurred due to hacks or bugs in the smart contract. This would not only protect the pool but also provide peace of mind to the stakers, knowing that their investments are protected.
Insurance in DeFi Lending Protocols
Lending protocols are another area where insurance can be used in DeFi. In lending, users deposit their tokens into a smart contract and earn interest on their deposits. The deposited tokens are then lent out to borrowers, who pay interest on the borrowed tokens. However, as with staking, there is always a risk involved in lending. The smart contract could be vulnerable to attacks or bugs, resulting in a loss of deposited tokens.
To address this risk, lending protocols can use insurance to protect against any losses incurred due to hacks or bugs in the smart contract. This would not only protect the protocol but also provide peace of mind to lenders, knowing that their deposited tokens are protected.
Insurance Platforms for Token Holders
In addition to protocols, individual users can also benefit from insurance in DeFi. With the volatility of the cryptocurrency market, users may want to protect their token holdings against any unexpected events. In this case, users can use insurance platforms that provide coverage against losses incurred due to price fluctuations or hacks.
These insurance platforms work by allowing users to pay a premium to insure their token holdings. In the event of a loss, the insurance platform would cover the insured amount. This provides users with a safety net and protects them against any unforeseen losses.
How Claims are made in DeFi protocols
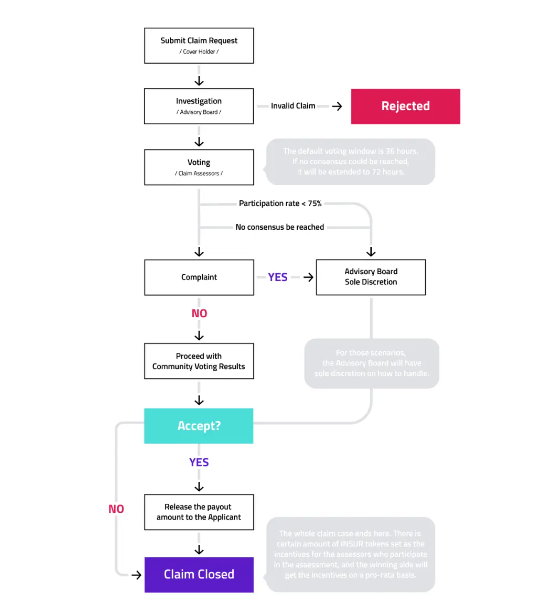
Case Study
Nexus Mutual
Nexus is arguably the most popular DeFi insurance protocol. Featuring a $230 million+ capital pool and claims paid out to the tune of over $9 million, the service is community-owned and run by a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO).
The platform works by having risk assessors stake the platform-native NXM token on various platforms. The stake makes up the various insurance pools, known as “Cover,” which will be distributed to claimants in the event that one of the covered scenarios (such as an exchange hack) occurs.
You can purchase insurance for different events by specifying which contract address you would like covered for and specifying how much cover you would like, as well as the period you’d like to be covered for.
The platform provides covers for –
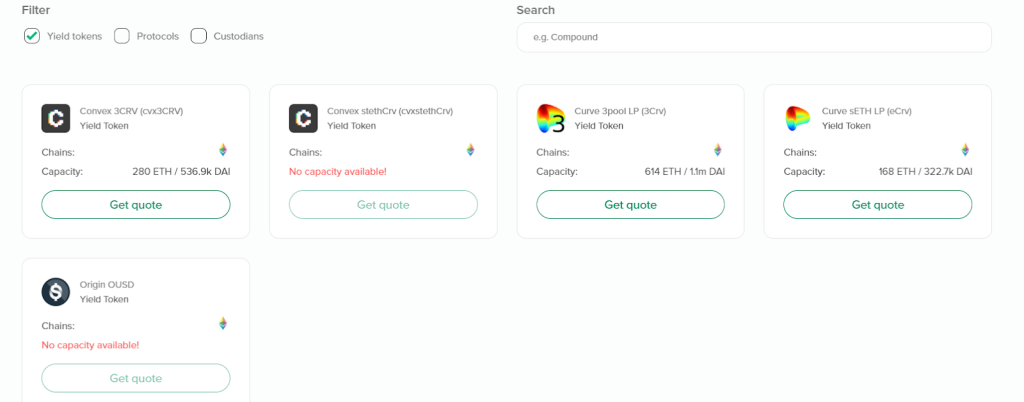
- Yield token cover: Protects against token de-pegging
This is the cover to protect funds from de-pegging risk on platforms like Curve and Convex. Other platforms also allow covers to protect the depegging of stablecoins
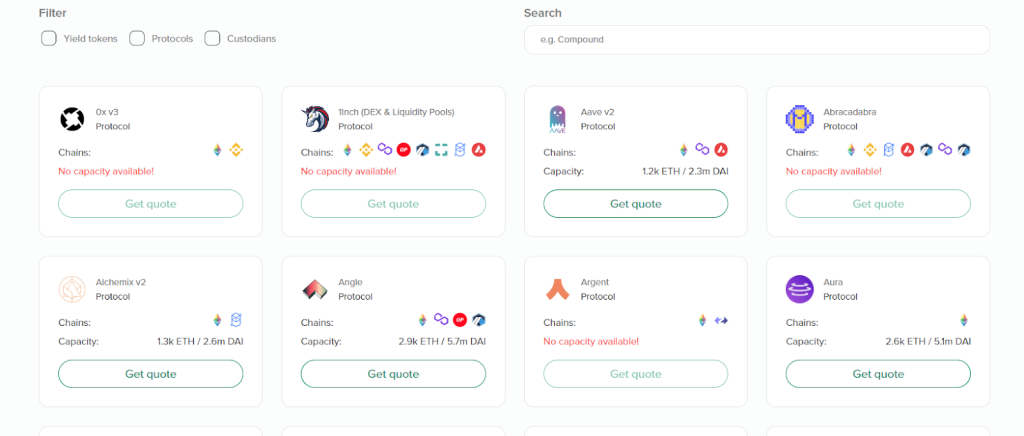
- Protocol Cover: Protects against hack of a specific protocol.
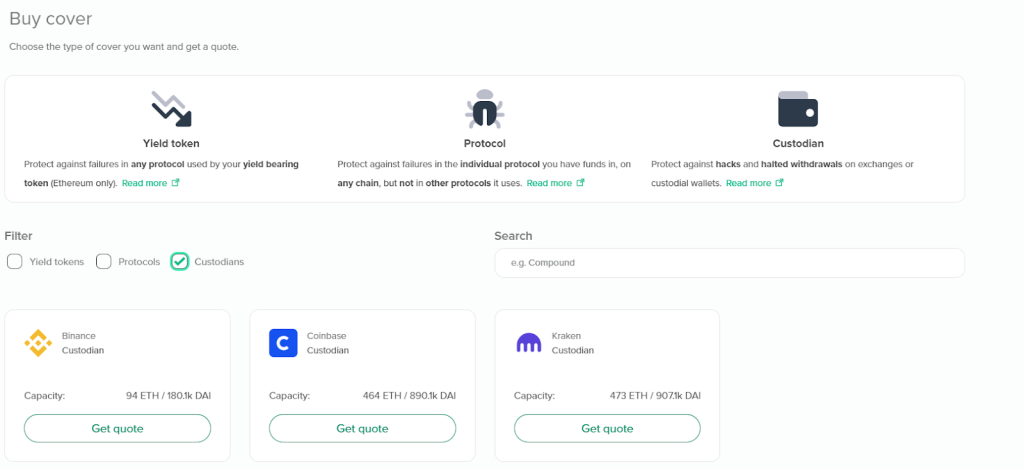
- Custody Cover: Protects against halted withdrawals on centralized exchanges
Conclusion
Insurance is an essential tool that helps protect individuals and organizations from the financial consequences of unforeseen events. The evolution of insurance has led to the development of new technologies, such as blockchain and DeFi, which have improved the efficiency and effectiveness of insurance products and services. Blockchain insurance has the potential to increase transparency and reduce fraud, while DeFi insurance provides coverage for vulnerable DeFi platforms. Understanding how insurance works and how funds










