Quick Links
The recent Bitcoin network congestion has been making headlines, temporarily suspending Bitcoin withdrawals on Binance, the world’s largest crypto exchange. This surge in unconfirmed transactions and the resulting backlog has raised concerns among investors and industry experts.
The Bitcoin network was overwhelmed with 390,000 unconfirmed transactions, leading to an increase in transaction fees. In response to the congestion, Binance increased its fees on withdrawals and began working to integrate the Lightning Network, a layer-two payments protocol for Bitcoin, to address the scalability issues. While other crypto exchanges like Coinbase and Kraken managed to dodge the congestion issue, it remains a significant concern for the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Efforts to address the congestion and scalability issues on the Bitcoin network are ongoing. One solution Bitcoin Core contributor Jeremy Rubin proposed involves cutting transactions in half to reliably smooth out network congestion and increase Bitcoin’s throughput during peak hours. While such solutions could improve network efficiency, the recent congestion highlights the challenges the Bitcoin network faces and the need for continued innovation and development to sustain its growth.
Understanding Bitcoin Network Congestion
Before we delve into the specifics, let’s first establish a clear understanding of what network congestion means in the context of the Bitcoin ecosystem. Network congestion refers to a situation where the number of transactions waiting to be processed surpasses the network’s capacity to handle them promptly. When congestion occurs, Bitcoin users may experience delays in transaction confirmations, increased fees, or even transaction failures.
Causes of Bitcoin Network Congestion
Various factors contribute to network congestion in the Bitcoin ecosystem. One primary cause is the increasing popularity and adoption of Bitcoin. The recent congestion was attributed to a recent spate of BRC-20 tokens & Bitcoin-based memecoins, such as Pepe, which have been clogging up the blockchain and driving up transaction fees. The issue has renewed concerns about the scalability and efficiency of the Bitcoin network. As more individuals and businesses embrace cryptocurrencies, the demand for Bitcoin transactions naturally escalates. Unfortunately, the current Bitcoin network infrastructure has limitations that can impede its scalability.
Another factor that exacerbates network congestion is the block size limit, which restricts the number of transactions that can be included in a single block. Bitcoin’s block size limit is set at 1 megabyte (MB), leading to a constrained throughput. This limitation becomes more pronounced with the growing number of transactions, resulting in increased congestion.
Impact of Bitcoin Network Congestion
The Bitcoin network congestion harmed the cryptocurrency’s value, with its price dropping by about 3.5% to $27,946.39, a fall of more than 5% since the prior Saturday. Over 55,000 traders were liquidated due to high transaction fees and the backlog of transactions.
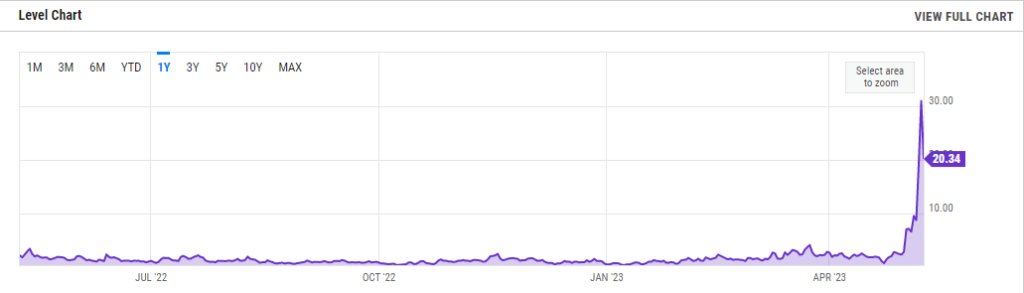
Bitcoin’s Average Transaction Fee is currently 20.34, down from 30.91 yesterday and up from 2.290 one year ago. This is a change of -34.19% from yesterday and 788.2% from one year ago.
Solutions to Bitcoin Network Congestion
Addressing network congestion is a top priority for the Bitcoin community, and various approaches are being explored to mitigate this issue. Here are a few potential solutions:
Segregated Witness (SegWit)
SegWit is a protocol upgrade implemented in 2017 that modifies the structure of Bitcoin transactions. By separating the witness data from the transaction data, SegWit reduces the size of transactions, allowing more of them to fit within a block. This optimization helps alleviate network congestion and lowers transaction fees.
Lightning Network
The Lightning Network is a second-layer protocol built on the Bitcoin blockchain. It enables off-chain transactions, which means that not every transaction needs to be recorded on the main blockchain. This scalability solution enhances the network’s capacity to handle more transactions and facilitates faster and cheaper micro-transactions.
Block size increase
Some proponents argue for an increase in the Bitcoin block size to accommodate more transactions per block. Expanding the block size limit could include more transactions, potentially reducing congestion. However, this approach has been debated within the Bitcoin community, as it may compromise the network’s decentralization and security.
Transaction batching and fee optimization
Bitcoin users and service providers can optimize their transactions by utilizing batching techniques. Instead of sending individual transactions, batching allows multiple transactions to be bundled together, reducing the overall burden on the network. Additionally, users can employ fee optimization strategies to ensure they are paying competitive fees while minimizing costs.
Layer 2 solutions
In addition to the Lightning Network, other Layer 2 solutions are being explored to alleviate network congestion. These solutions involve building parallel networks or sidechains that can process transactions off the main Bitcoin blockchain, thus reducing the burden on the primary network.
Improved fee estimation algorithms
Enhancing the accuracy of fee estimation algorithms can help users determine appropriate transaction fees based on the current network conditions. This can prevent overpaying during congestion and ensure transactions are processed efficiently.
Continued research and development
The Bitcoin community is constantly engaged in research and development efforts to identify innovative solutions for network congestion. This includes exploring technologies like Schnorr signatures, Graphene, and more efficient transaction relay protocols.
Conclusion
Bitcoin network congestion challenges the efficiency and scalability of the leading cryptocurrency. However, the community is working on various solutions to address this issue. Through protocol upgrades, off-chain transaction mechanisms, and optimization techniques, progress is being made to alleviate network congestion, reduce transaction fees, and improve overall user experience.
As Bitcoin continues to evolve, users and businesses must stay informed about the latest advancements and best practices in navigating network congestion. By implementing strategies such as fee optimization, transaction batching, and leveraging Layer 2 solutions, individuals can mitigate the impact of congestion and ensure smoother Bitcoin transactions.













